Immunity is the body’s ability to fight off foreign invaders, such as viruses and bacteria. At the heart of this important defense system are the thymus gland and T-cells, which we’ll discuss in this article, including what they are, how they function, and how they relate to T-cells.
Definition and Location of the Thymus
The thymus is a crucial organ in our immune system located in the upper chest, just behind the sternum and above the heart. It aids in the maturation and differentiation of T cells.
Form and Structure of the Thymus
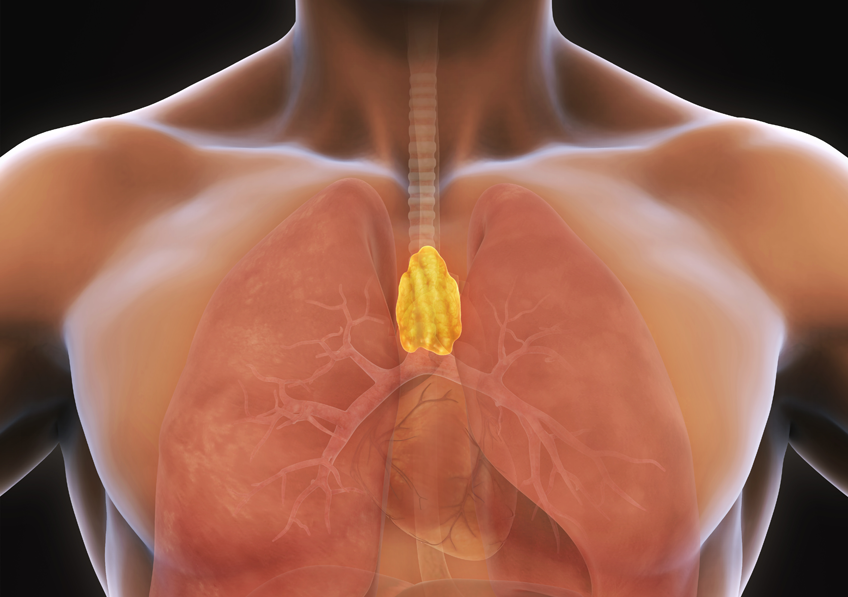
The thymus has a leaf-like shape, divided into two lobes, each further divided into many lobules. These lobules contain an outer cortex and an inner medulla, where T cells mature.
Function of the Thymus
The primary function of the thymus is to produce and mature T cells, which are essential for recognizing and attacking pathogens.
Related Diseases
Diseases related to the thymus include thymoma (thymus tumor) and myasthenia gravis, an autoimmune disorder.
Thymus and T Cells
The thymus is akin to a “school” for T cells, where they learn to distinguish between self and non-self antigens before regulating immune responses throughout the body.
Roles of T Cells
T cells have two main roles: directly attacking infected or cancerous cells and regulating other immune cells’ activities.
Ways to Boost Immunity
-
Balanced Diet
- Consume foods rich in vitamins and minerals.
- Eat antioxidant-rich fruits and vegetables.
-
Regular Exercise
- Engage in aerobic exercise 3-5 times a week.
- Include strength training.
-
Sufficient Sleep
- Ensure 7-9 hours of sleep each night.
- Maintain a consistent sleep schedule.
-
Stress Management
- Practice meditation or yoga.
- Enjoy hobbies.
-
Hydration
- Drink at least 8 glasses of water daily.
- Limit alcohol and caffeine intake.
-
Healthy Lifestyle
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol.
- Have regular health check-ups.
-
Vaccinations
- Get necessary vaccinations like flu and pneumonia shots.
-
Maintain Healthy Weight
- Keep a balanced weight.
- Avoid being overweight or underweight.
-
Personal Hygiene
- Wash hands frequently.
- Maintain good personal hygiene to prevent infections.